Fever in Children
What are Febrile Convulsions?
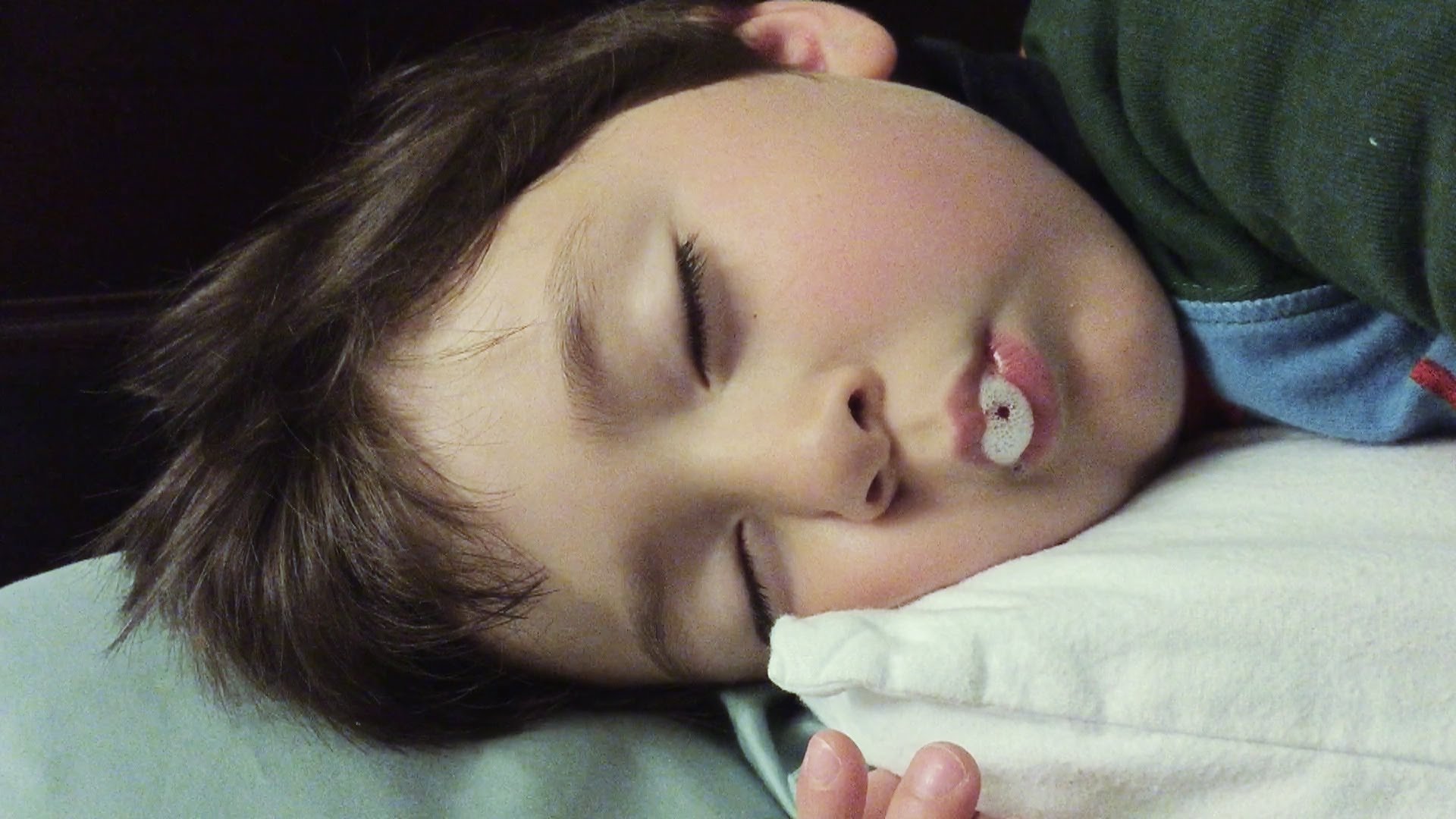 |
Febrile convulsions are fits or seizures that occur in young children when they have high fever. A convulsion is a sudden event when the child is not quite with it starts to jerk or twitch and may have difficulty in breathing. |
WHAT CAUSES FEBRILE CONVULSIONS?
They only occur when the child has a high temperature. The growing brains of little children are more sensitive to fever than are more mature brains, and when the normal brain activity is upset, a fit can occur.
The fever is caused by an infection, which is usually a viral infection and often is not obvious. A simple viral infection that would give an adult a heavy cold is the type often responsible. Sometimes an infected ear or throat or bladder may be found by the doctor.
WHO GETS FEBRILE SEIZURES?
They are common and can affect any normal child. About 5 in every 100 children will have a fit from a fever. They tend to run in families.
They usually occur in children from 6 months to 3 years of age, the commonest age range being from 9 months to 20 months; they usually stop by 6 years of age.
WHAT ARE THE RISKS OF FEBRILE CONVULSIONS?
Febrile convulsions (whether one or several) in normal children do not usually cause brain damage, mental retardation or epilepsy. Most children are absolutely normal later on.
HOW DO YOU MANAGE A CONVULSION OR SEIZURE IN CHILDREN?
1. Place the child on his or her side, chest down, with the head turned to one side. Never lie a fitting child on his or her back. Do not force anything into the child’s mouth.
2. Obtain medical help as soon as possible. Ring or go to your local doctor or to your nearest hospital. Even if the fits stops, have your child checked.
HOW DO YOU HELP PREVENT ANOTHER EPISODE?
Because some children have further febrile convulsions, it is important to manage any fever as soon as it is noticed. Undress the child down to singlet and underpants, keep the child cool, and give fluids and paracetamol mixture.
KEY POINTS
- Febrile convulsions may occur again
- They usually occur from 6 months to 3 years of age
- They cause no long-term problems
- They do not cause death, brain damage or epilepsy
- They stop by 6 years of age
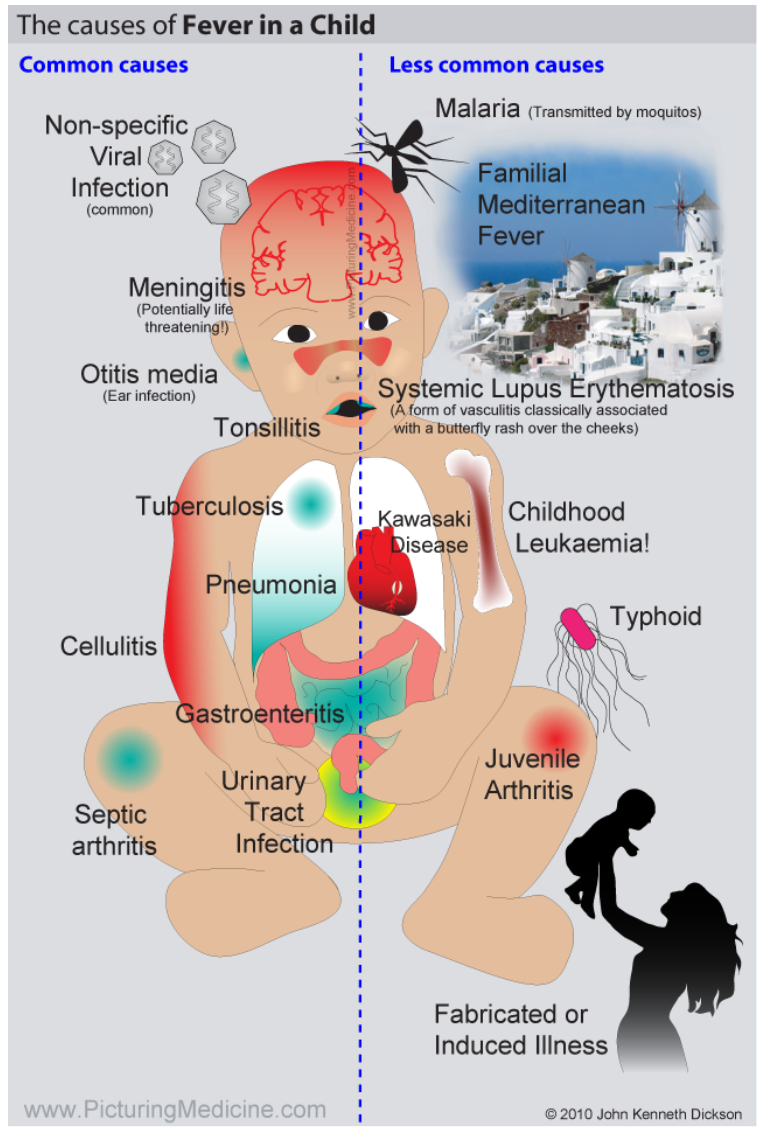
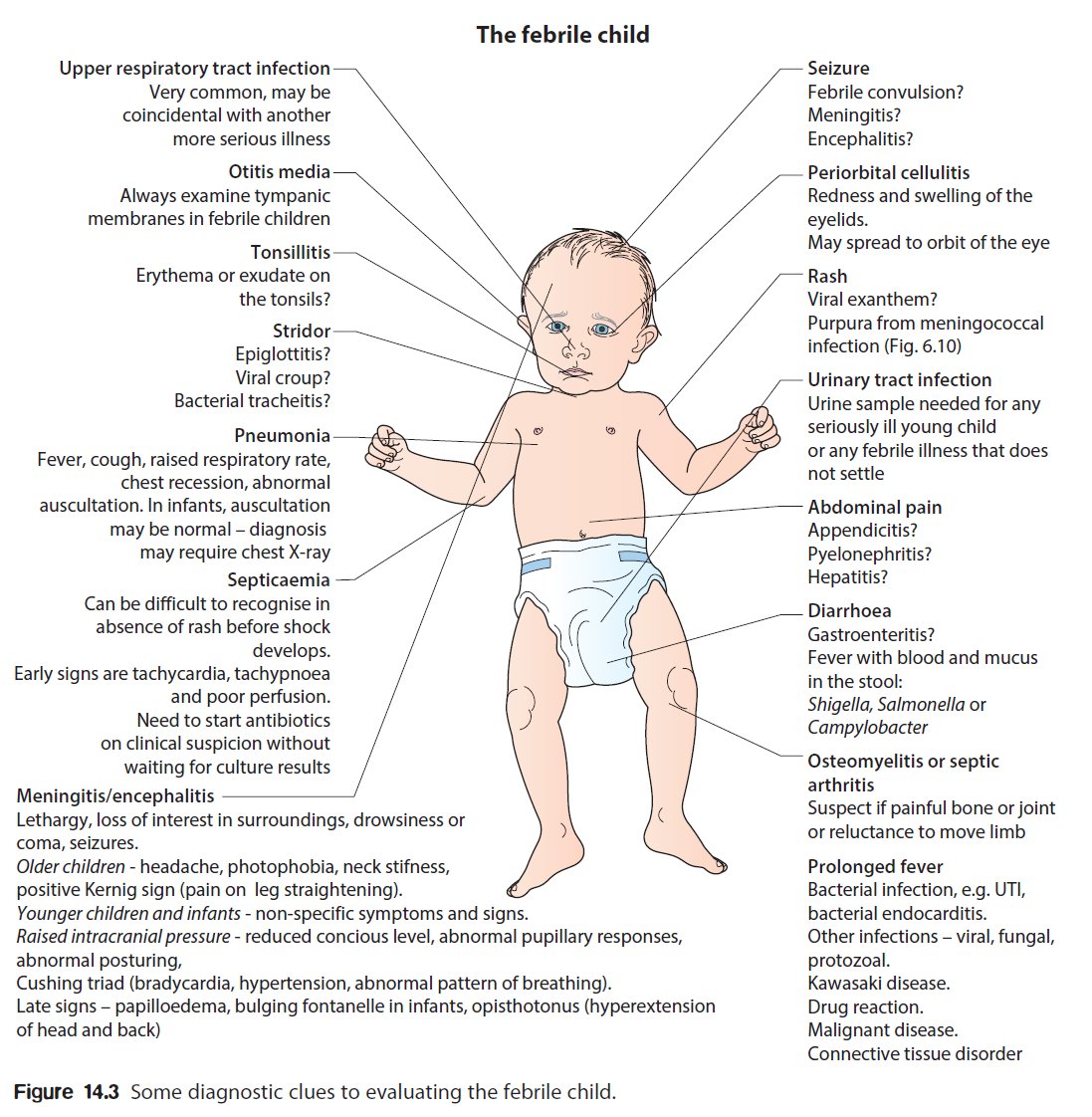
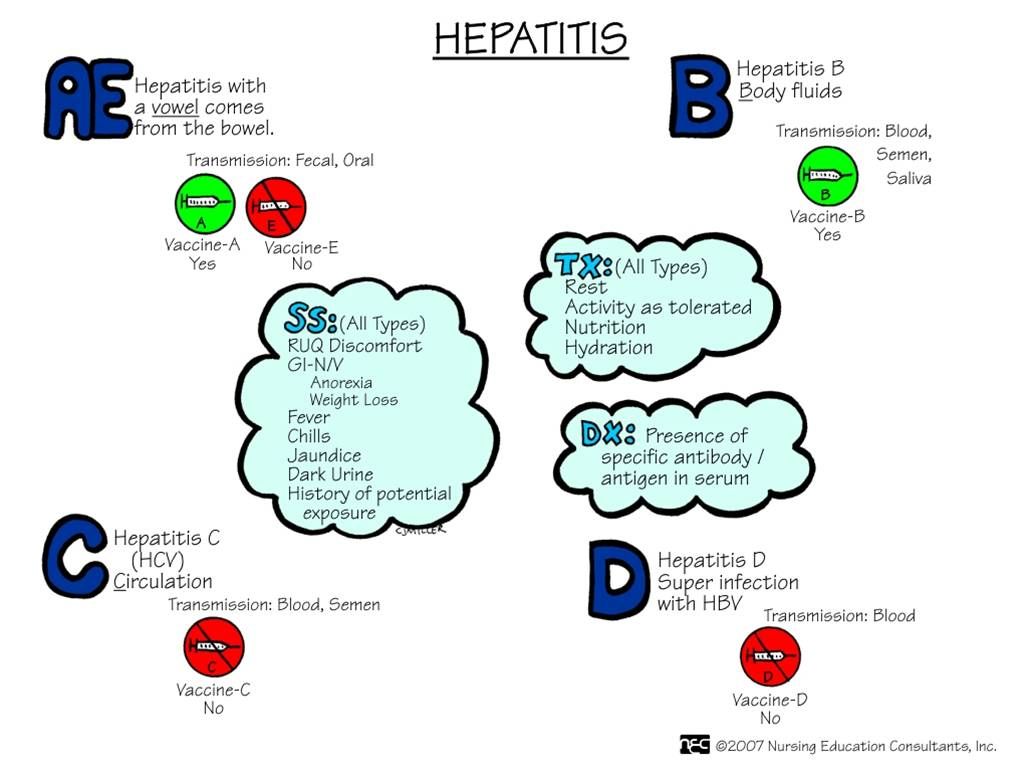
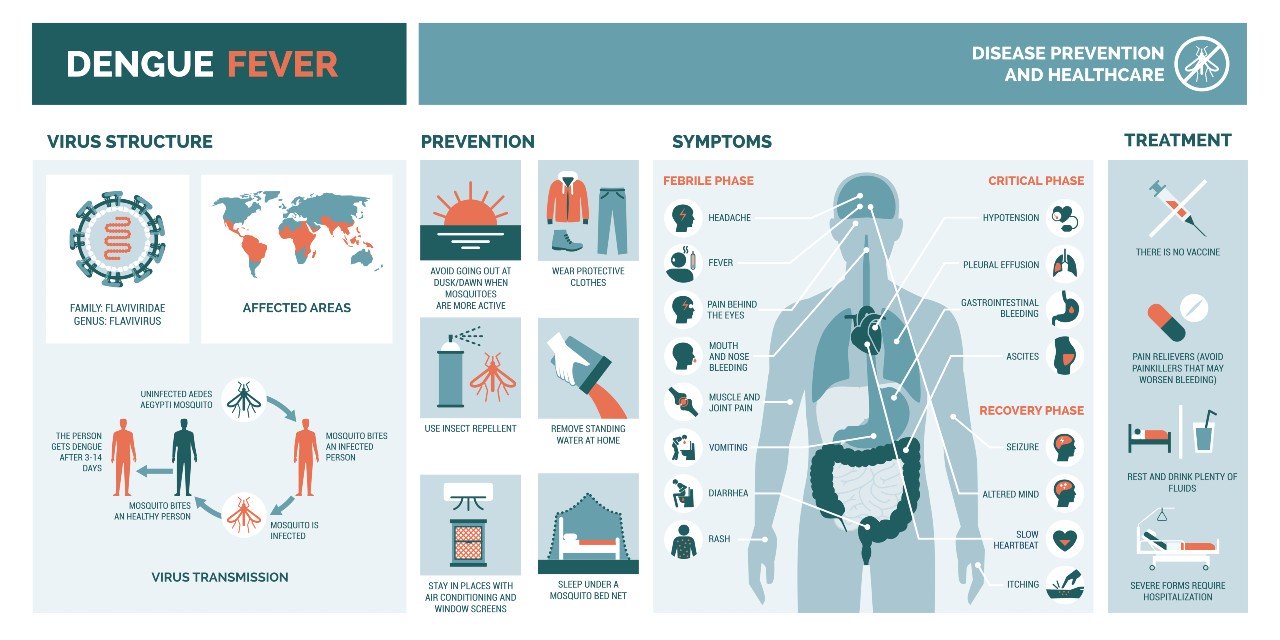
Other Possible Causes of Fever in Children
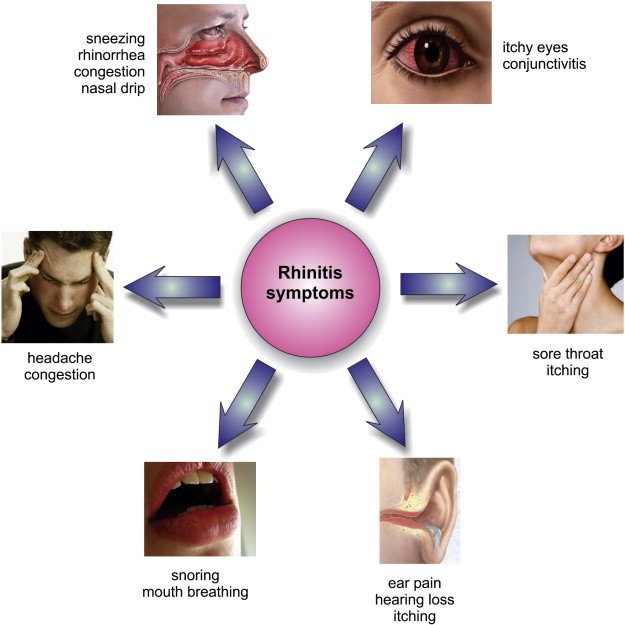
Ear, Nose & Throat Problems
Skin Problems - Treatment for Allergies, Dermatitis, Eczema & Urticaria/Hives
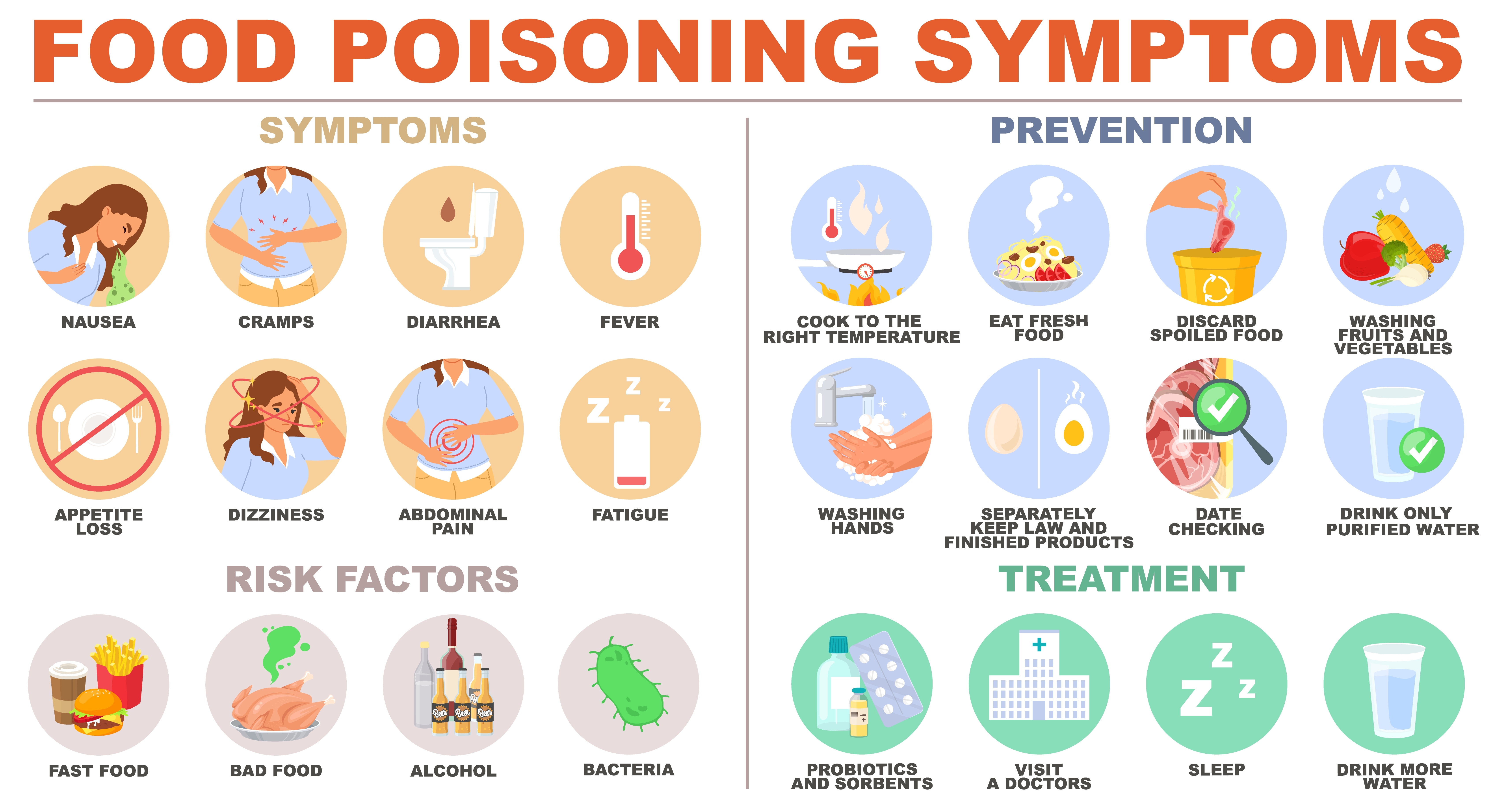
Diarrhea Treatment, Learn what is Gastroenteritis, Management of Irritable Bowel Syndrome & Heartburn or GERD
|
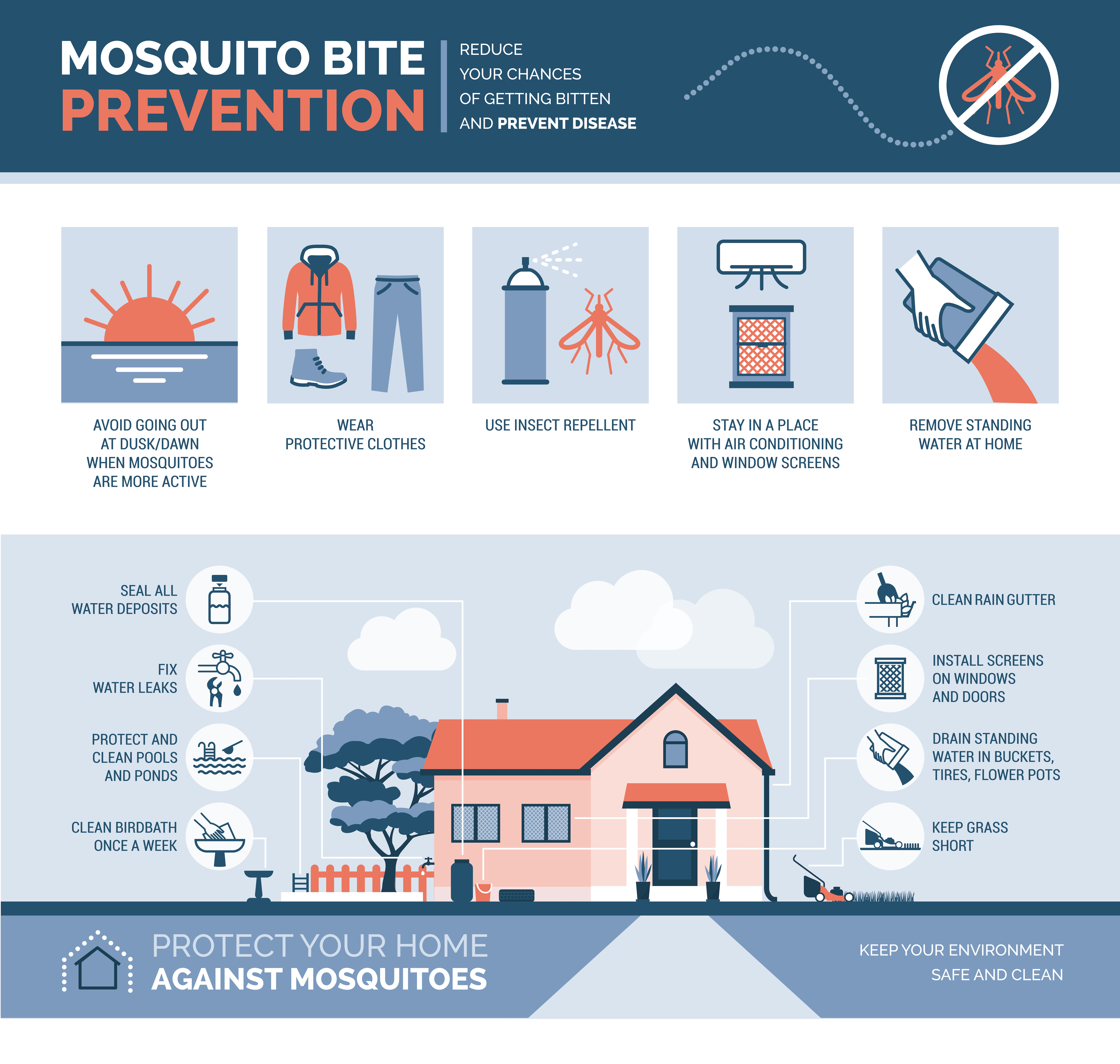
Infectious Diseases - Dengue Fever, Influenza, Hepatitis B, COVID-19
The information provided in this website is for knowledge purposes only. It does not constitute medical advice.
Should you encounter any medical problem that you are unsure of, always consult your doctor or health care provider for assistance and medical advice.